Antwort What are the 4 types of ontology? Weitere Antworten – What are the 5 elements of ontology

Ontology – What are the 5 elements of ontology The process of knowledge formalization in ontologies is built upon five key components: classes, instances, relations, functions, and axioms [1].Broadly speaking, three distinct ontological positions identified are realism, idealism and materialism (Snape & Spencer 2003).Lowe's four-category-ontology. The four categories are object, kind, mode, and attribute. The fourfold structure is based on two distinctions. The first distinction is between substantial entities (objects and kinds) and non-substantial entities (modes and attributes).

What is ontology in simple words : Ontology, at its simplest, is the study of existence. But it is much more than that, too. Ontology is also the study of how we determine if things exist or not, as well as the classification of existence. It attempts to take things that are abstract and establish that they are, in fact, real.
What is ontology vs epistemology
What is the Difference Between Ontology and Epistemology The difference between ontology and epistemology comes down to the kinds of questions that each branch of philosophy asks. If ontology asks what exists, then epistemology asks, and how do people know what exists
What is an example of ontology in real life : An ontology is a study of what things exist. An example would be fundamental physics. This discipline is in the business of determining which particles exist. The atom, proton, and quark are examples of the refining process of determining physical ontology.
It refers to your view of reality and to what extent it exists 'out there', to be captured through research. Ontology is concerned with what is true or real.

Ontology comes from two Greek words: on, which means "being," and logia, which means "study." So ontology is the study of being alive and existing.
What is a good example of an ontology
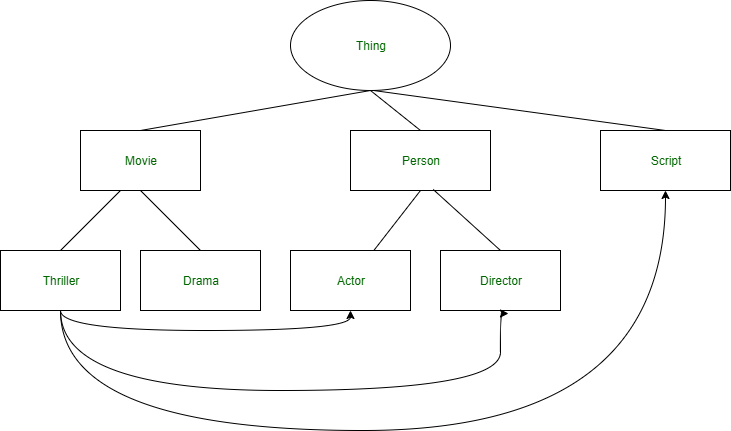
At its core, ontology is the study of what is. To make this a little more concrete, one could also say ontology is the study of what exists or of what is real. “Does God exist,” “Are my feelings real”, “What is 'nothing,' and does it exist” are all examples of ontological questions.Ontology defines your research framework while epistemology determines the research questions that you will need to answer. Together, ontology, epistemology and methodology form an all-encompassing system of interrelated practice and thinking that defines the nature of your research.The first branch is ontology, or the 'study of being', which is concerned with what actually exists in the world about which humans can acquire knowledge. Ontology helps researchers recognize how certain they can be about the nature and existence of objects they are researching.
Ontology: is the philosophical study of being. It refers to your view of reality and to what extent it exists 'out there', to be captured through research. Ontology is concerned with what is true or real.
What is difference between ontology and epistemology : What is the Difference Between Ontology and Epistemology The difference between ontology and epistemology comes down to the kinds of questions that each branch of philosophy asks. If ontology asks what exists, then epistemology asks, and how do people know what exists
How do I create my own ontology : Basic recipe to start building an ontology
- Write down the use cases for the ontology (see above).
- Make a table of all similar ontologies that exist, within and outside OBO (this requires research, and is an essential part of the process).
- Determine whether you have something to start from.
- Gather your tools.
What comes first epistemology or ontology
Epistemology and methodology are driven by ontological beliefs and observations. Ontology is the belief upon what you base your research. It specifies the nature of something that we can sense and that we wish to investigate further if we are to know more about and understand an event or phenomenon.
Science often uses both ontological and epistemological questions when framing research objectives and exploring new knowledge about the universe.Ontology is concerned with what is true or real. Epistemology: is the 'theory of knowledge'. It refers to the principles of what can be known and how you can know it; that is, how you can find out about it.
What is an example of ontology : At its core, ontology is the study of what is. To make this a little more concrete, one could also say ontology is the study of what exists or of what is real. “Does God exist,” “Are my feelings real”, “What is 'nothing,' and does it exist” are all examples of ontological questions.

![csm_2405-bauerfeind-produktkategoriesseiten-bandagen-ellenbogenbandage-2560x1400_88-1_f91f66009c[1]](https://www.nakajimamegumi.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/csm_2405-bauerfeind-produktkategoriesseiten-bandagen-ellenbogenbandage-2560x1400_88-1_f91f66009c1-1024x521-65x65.jpg)
![Ischiasschmerzen[1]](https://www.nakajimamegumi.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/Ischiasschmerzen1-1024x640-65x65.jpg)
![csm_blogbeitrag_autoimmunerkrankung_d307ac8b72[1]](https://www.nakajimamegumi.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/csm_blogbeitrag_autoimmunerkrankung_d307ac8b721-1024x576-65x65.jpeg)